Automotive
Understanding the Window Motor: The Heart of Power Windows
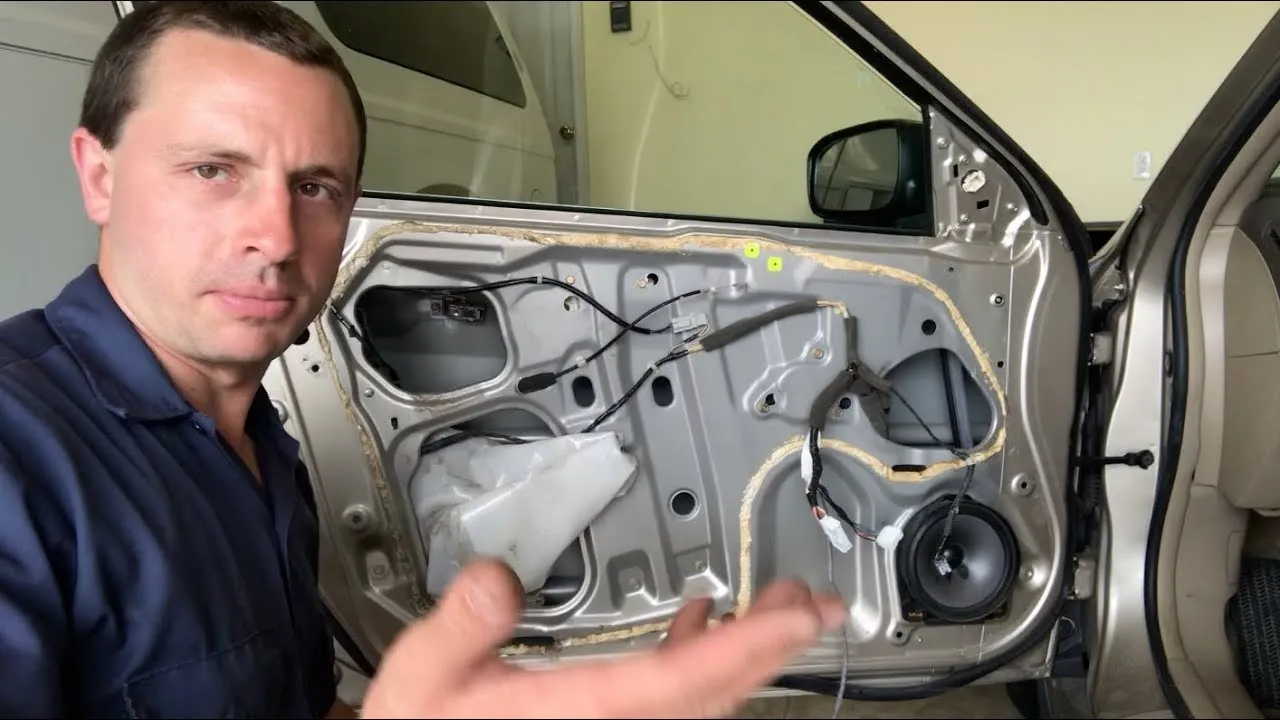

Power windows have become a standard feature in modern vehicles, offering convenience, comfort, and functionality to drivers and passengers alike. At the core of power windows lies the window motor, a crucial component responsible for converting electrical energy into mechanical motion to raise and lower the windows. Despite its importance, the window motor is often overlooked until it malfunctions, leading to frustration and inconvenience for vehicle owners. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the intricacies of the window motor, exploring its function, components, and maintenance requirements to help you gain a better understanding of this essential automotive component.
The Function of the Window Motor:
The window motor is a small electric motor located inside the door panel of the vehicle, near the window regulator mechanism. Its primary function is to generate rotational motion when activated by the window switch, which in turn moves the window regulator to raise or lower the window glass.
When the window switch is pressed, electrical current is sent to the window motor, causing it to rotate in one direction or the other, depending on the desired direction of window movement. The rotational motion of the motor is transferred to the window regulator through a series of gears or cables, which then moves the window glass up or down along its track. For more information on window repairs and services, you can visit Omni Auto Glass website, where experts can assist with any issues related to automotive glass.
Components of the Window Motor:
The window motor consists of several key components that work together to facilitate smooth and efficient window operation:
- Electric Motor: At the heart of the window motor is an electric motor that converts electrical energy into mechanical motion. The motor is typically equipped with brushes and a commutator, which enable it to generate rotational force when current is applied.
- Gearbox: The motor is connected to a gearbox or gearset that helps to control the speed and torque of the motor’s output. The gearbox may consist of gears, pulleys, or cables, depending on the design of the window motor.
- Encoder: Some modern window motors are equipped with an encoder or position sensor that provides feedback on the position of the window glass. This allows the motor to accurately control the movement of the window and prevent over-travel or binding.
- Mounting Bracket: The window motor is mounted inside the door panel using a sturdy bracket or mounting plate. This helps to secure the motor in place and prevent excessive vibration or movement during operation.
Types of Window Motors:
There are two main types of window motors commonly used in vehicles:
- Direct-Drive Motors: Direct-drive window motors are the most common type and are typically found in older vehicles. These motors feature a simple design with a central rotor connected directly to the window regulator mechanism. When activated, the motor rotates the rotor to raise or lower the window glass.
- Worm Gear Motors: Worm gear window motors are a more modern design and are commonly used in newer vehicles. These motors utilize a worm gear mechanism to convert the rotational motion of the motor into linear motion, which is then used to move the window regulator and window glass.
Both types of window motors have their advantages and disadvantages, and the choice between them often depends on factors such as cost, space constraints, and performance requirements.
Common Issues and Maintenance:
Like any mechanical component, window motors are subject to wear and tear over time, which can lead to malfunctions and performance issues. Some common problems associated with window motors include:
- Motor Failure: Over time, the motor brushes, bearings, or windings may wear out, leading to motor failure. This can result in sluggish or inconsistent window movement, unresponsive power windows, or complete window motor failure.
- Gearbox Wear: The gears, pulleys, or cables in the gearbox may become worn or damaged, leading to poor window operation or excessive noise during window movement.
- Electrical Issues: Electrical problems, such as blown fuses, corroded connectors, or damaged wiring, can also affect the performance of the window motor. These issues may cause intermittent window operation, erratic behavior, or complete power window failure.
To prevent issues with the window motor, it’s essential to perform regular maintenance and inspection of the power windows. This includes lubricating the window regulator tracks, cleaning the window switch contacts, and checking the electrical connections for signs of corrosion or damage. Additionally, if you notice any symptoms of window motor failure, such as slow or erratic window movement, it’s important to have the motor inspected and repaired by a qualified mechanic to prevent further damage and ensure proper operation of the power windows.
Conclusion:
The window motor is a critical component of power windows, providing the mechanical motion necessary to raise and lower the window glass with ease. Understanding the function, components, and maintenance requirements of the window motor can help vehicle owners identify issues early, perform necessary repairs, and ensure smooth operation of their power windows. By staying proactive and attentive to the condition of the window motor, you can avoid inconvenience and frustration caused by power window malfunctions and enjoy reliable performance for years to come.

Automotive
The Top Ways To Provide Ongoing Protection For Your Car In Australia

It is true that we have cars to take us here and there to the office, to the shopping mall and taking the kids to school and back. This is not its primary purpose, however, because everything nowadays is about providing good first impressions and the vehicle that you drive around in does that very thing. This is why you need to do whatever you can to maintain your car’s interior and exterior at all times. Putting preventative measures into place is better than just waiting for the problem to occur and then addressing it.
This is one of the reasons why you need to invest in an affordable retractable car shade because this is the one thing that can protect your vehicle from not getting warmer on the inside and it protects your dashboard, your carpets and your seats. This is just one of the top ways to provide protection for your car in Australia and the following are some others that you might want to consider.
- Wash your vehicle regularly – This means doing it by hand and not bringing into those automatic car washes that do more harm than good. You need to remove dirt and debris as soon as it appears on your vehicle and have a system in place where you wash the car first with a reputable cleaning solution and then rinse it off well afterwards.
- Park with the car in mind – We do get a lot of sunshine here in Australia and so you have to take measures when you’re parking your car away from your home. Always try to find shade whenever possible and if there is a tree to park under, then that is where you go. You will, of course, have your car shade, but it needs a little bit of help as well.
- Get your vehicle coated – What is being referred to here is a ceramic coating that gives your paint a kind of shield that is working all the time to stop scratches from happening. It also makes the car a lot easier to wash and maintain.
These are solutions for the outside of your vehicle, but pay attention to the inside as well, especially under the bonnet. Get your engine serviced on a regular basis so that the oil and filter are replaced whenever they need to be.
Automotive
To Avoid Downtime You Should Replace the Pneumatic Silencer at Frequent Intervals!
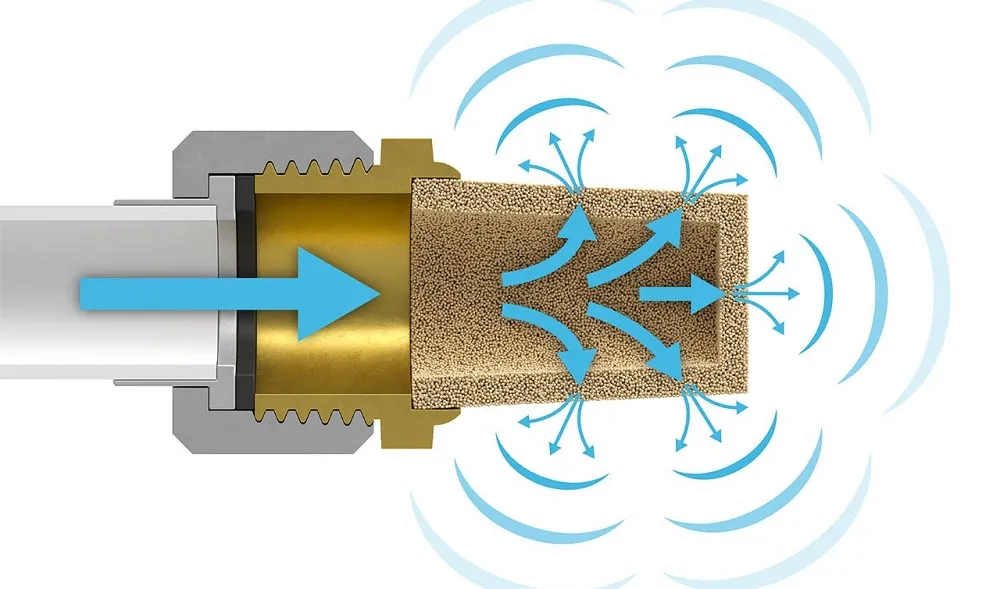
Pneumatic silencer, also called a muffler, are used in the automotive sector to lower the sound that happens when compressed air passes through the exhaust ports of the valve. Many scientists and experts have claimed that this noise is one of our biggest environmental hazards. Therefore, it is crucial that this noise is eliminated to lower the risk. In order to ensure that these mufflers offer the right service, it is essential that they should be replaced when necessary. Some companies remove the mufflers to minimize the downtime risk, but this tends to negatively impact the worker’s health and the environment.
Pneumatic silencers can reduce the sound level to a great extent
With the right technique it is possible to almost reduce most of the machine noise. Most of the machines have several mufflers to deal with the noise. This tool helps to divide the compressed air through multiple small holes to increase the frequency of sound to a level that is not harmful to the human ear. With the help of this tool, it is possible to reduce the sound level to 30-40 dB(A). This is significant since reducing the sound by 10 dB(A) is often considered to halve the sound level. This is often beneficial because:
- It lowers the risk of hearing damage and hearing ailments like tinnitus and hearing loss,
- It improves the overall work environment,
- And finally, it enhances the overall performance of the worker
Old mufflers can cause downtime and you have to replace them after a certain point of time. The flow through the tool will go down due to the accumulation of dirt particles which will clog the filter. The lower flow can be due to multiple reasons, such as:
- Presence of impurities in the compressed air,
- Presence of dirt in the pipes,
- Operating lubrication from the machine.
This is a very common problem in the industry. If the filter gets clogged, the compressed air gets stuck and creates a counterpressure on the valve. Therefore, it becomes all the more essential to identify the problems and replace the mufflers as soon as possible. A clogged muffler not only lowers the machine’s working potential but can also affect safety and lead to downtime risks. If the pressure gets too high, it can cause the muffler to explode.
Which muffler should you change?
When planning the downtime, it is best to examine all the possible mufflers and replace the clogged ones. This is an easy solution because some mufflers come with built-in warning indicators. If you find that there are indications of the muffler being clogged, then you should get it replaced ASAP. In case you are unsure, go ahead and replace all the mufflers—the ones that are working and the ones that are faulty. However, this will be an expensive solution since you have to replace all of them.
Alternate solution:
There is another solution that you can opt for. Why don’t you install a breather vent? This tool is very effective because when you install it, you can enjoy the following:
- This vent helps to equalize the pressure inside the container or the system,
- It helps to keep out the dirt, dust and moisture from the filter,
- It prevents the tanks from exploding due to the increase of the pressure inside the tank,
- It reduces corrosions and emissions,
- And finally, it helps to improve the overall safety of the equipment.
Summing it up: Without any delay, the moment you identify that the muffler is creating issues, you should get it replaced. Find out who are the leading dealers of pneumatic silencers and breather vents in your city. Get in touch with them as and when needed.
Read More latest Posts
Automotive
Embracing Outdoor Adventures with Grundig E-Bikes: Sustainable Lifestyle and Quality Connections

E-bikes are reworking outside experiences by blending the thrill of cycling with a high-tech boost. Grundig’s e-bikes stand out in this area, imparting sustainability and exceptional reviews in natural settings. With eco-friendly benefits, zero emissions, and supportive capabilities for riders of various ability tiers, the Grundig e-bike concept presents a really perfect choice for the ones searching for an environmentally aware and fun lifestyle.
E-Bikes and Eco-Friendly Mobility
Grundig e-bikes provide zero carbon emissions, a key gain for eco-conscious people. Unlike gas-based totally automobiles, these e-bikes produce no harmful exhaust, allowing customers to experience their adventure even while minimizing their carbon footprint. For those concerned about environmental impact, Grundig’s e-bikes enable customers to experience a low-emission lifestyle without sacrificing consolation or mobility.
Grundig gives fashions geared up with durable motors designed for electricity performance, making sure an easy journey over lengthy distances. This makes them a perfect opportunity for traditional motors for commuting, permitting riders to avoid site visitors while embracing an eco-friendly tour alternative.
Exclusive Usability and Versatile Features
Grundig e-bikes are constructed in the progressive era and have consumer-pleasant designs, making them reachable to numerous riders. The GCB-1 and ETB2800 models, for example, integrate effective vehicles that allow riders to tour over distinct terrains easily. Grundig’s attention to ergonomic designs and excellent components additionally makes these bikes easy to perform, giving customers more desirable balance and control.
The mid-engine placement complements weight distribution, providing dynamic help that adjusts to riding situations. Whether tackling steep trails, going for leisurely rides, or wearing masses, Grundig e-bikes’ versatility makes them appropriate for any adventure. Riders can navigate challenging routes with the peace of mind of a dependable and adaptive era that enhances their herbal power and movement.
Lifestyle Benefits: Closer Connections with Nature, Friends, and Family
Beyond green advantages and technology, Grundig e-bikes promote a lifestyle that emphasizes quality time with loved ones. E-bike excursions foster a unique way to bond with buddies or circle of relatives members with the aid of sharing scenic trails, exploring new paths, or even organizing group rides. By replacing noisy, gas-driven vehicles with these silent, green e-bikes, riders can immerse themselves in the sounds and sights of nature, making outdoor time feel more proper and worthwhile.
E-bikes are, in particular, attractive for outside lovers who respect the balance of nature with a touch of comfort. With capabilities that lessen the strain on longer trips, Grundig e-bikes permit riders of different ability ranges to experience prolonged trips without physical discomfort, making them best for casual family outings and group rides alike. This accessibility opens up opportunities for all of us, from novices to pro cyclists, to share in the experience of cycling collectively, creating lasting reminiscences and deeper connections.
Health and Wellness Perks of E-Bike Riding
Incorporating e-bike rides right into a weekly recurring can yield sizable well-being benefits. E-cycling combines aerobic exercising with low-effect aid, which means riders can improve their cardiovascular health and average health tiers while reducing joint pressure. This stability encourages normal physical interest, which is critical for retaining bodily and mental well-being. Grundig e-bikes allow users to regulate the extent of help so riders can manipulate their intensity and revel in the bodily advantages without overexerting themselves.
Riding in herbal environments additionally benefits mental fitness, decreasing strain stages and fostering a feeling of relaxation and mindfulness. E-motorbike rides encourage people to step far from screens, spend more time outside, and disconnect from everyday stresses, creating a pathway to intellectual rejuvenation.
E-Bikes for Daily Convenience and Exploration
Grundig’s e-bikes are properly suitable for city commuting, short errands, or extended rides in the natural environment. As a bendy mode of transport, they make short-distance commuting clean and exciting, even putting off some of the hassles related to vehicle journeys, including parking and fuel expenses. This makes e-bikes, in particular, attractive to city dwellers who need efficient, hassle-free travel and people in rural areas looking to discover widespread trails.
Their ease of use additionally aligns with the growing fashion in the direction of multi-modal transport. E-bikes can complement public delivery or act as a dependable automobile substitute for quick to medium distances. Grundig’s models, geared up with effective batteries, allow riders to cover giant distances at an unmarried price, giving customers the freedom to discover without worrying about recharging.
Cost-Efficiency and Low Maintenance
Switching to e-bikes may be a cost-effective desire. Grundig’s e-bikes have minimal gas and renovation charges in comparison to traditional automobiles, as there are no gasoline fees and fewer mechanical elements to service. While the preliminary funding can also seem huge, the long-term savings in fuel, parking charges, and maintenance make e-bikes an intelligent financial selection. Furthermore, with Grundig’s exceptional substances and dependable guarantee, users can believe that their e-bikes will offer a lengthy period of cost and performance.
Conclusion
Grundig’s e-bikes encapsulate the destiny of sustainable mobility while promoting a lively, nature-connected lifestyle. Their zero-emission operation, versatility, and luxury functions lead them to be an attractive choice for every person trying to experience the outdoors in an eco-conscious way. These e-bikes offer customers greater than just a mode of delivery; they provide a gateway for high-quality experiences, whether or not commuting, exploring nature, or bonding with pals and their own families.
As extra humans prioritize sustainability, health, and first-class time, Grundig e-bikes end up a super answer, blending the pleasantness of technology and eco-aware layout. They invite humans to embody an adventurous, wholesome lifestyle while having a nice effect on the surroundings, redefining the way we view outdoor excursions and each daily commute.
-

 Travel1 year ago
Travel1 year agoOnboardicafe.com Login Exploring the Delights of Onboardicafe
-

 Food & Recipes1 year ago
Food & Recipes1 year agoFive Food Products You Must Avoid Giving to Your Infant
-

 Sports1 year ago
Sports1 year agoThe Most Popular Sports In The World
-

 Technology6 months ago
Technology6 months agoSustainable Practices in Video Production: Reducing the Carbon Footprint
-

 Sports11 months ago
Sports11 months agoSmart Solutions for Football Field Maintenance
-
 Health & Fitness12 months ago
Health & Fitness12 months agoSuboxone Tooth Decay Lawsuits and the Pursuit of Justice Against Indivior
-

 Sports10 months ago
Sports10 months agoWearable Tech and the Future of Football
-

 Entertainment1 year ago
Entertainment1 year agoNavigating the Web: The Ultimate List of Tamilrockers Proxy Alternatives









